Introduction
If you are a former trucker who wants to enter the brokerage side of trucking then you are at the correct resource page. Our resource will guide you on your training path as you learn, how to become a freight broker even if you have little to no experience.
Freight brokers are an important part of the trucking and transportation supply chain.

Almost all the products you will encounter in your life have been transported by truck at one point in time.
Speaking of economic statistics, the logistics and transportation industry in the United States alone was totaled at $1.48 trillion in 2015.
Many brokers are inactive which paves the way for aspiring brokers to set up a successful business.
In fact, a transportation law called Moving Ahead Progress (MAP-21), signed by President Barack Obama on July 6, 2012, brought significant changes to the trucking sector. This law increased the barrier to entry for trucking.
The introduction aside, this step by step guide on how to become a freight broker will help you reach your goal.
Step 1: Understand the job description of a freight broker and how much money can be made
 A freight broker acts as the middlemen between shippers and carriers. There job is to negotiate good shipping rates and fast delivery times with transportation companies.
A freight broker acts as the middlemen between shippers and carriers. There job is to negotiate good shipping rates and fast delivery times with transportation companies.
The broker will work directly with the shipper to negotiate a rate.
Over time, they will build strong business relations with both carriers and shippers.
The legal definition of a broker can be located here.
Freight broker salary
The amount of money that you can earn being a freight broker varies depending on the situation.
Independent brokers running their own freight brokerage have far more income potential than brokers working for an existing business. An independent freight broker can generate earnings in the six figure ($100,000 +) range.
As a proof of concept designed to teach you the amount of money in the industry, the profits of the top 5 freight brokerages are listed below:
| Company | Net Profit |
| C.H. Robinson Worldwide | $1,718 million ($1.7 billion) |
| Total Quality Logistics | $445 million |
| XPO Logistics Inc. | $342 million |
| Echo Global Logistics | $290 million |
| Coyote Logistics | $280 million |
Surely now you can understand the potential a freight brokerage has. However, it is not guaranteed that anyone can succeed. You can prosper only if you dedicate the time to learn the required skills, planning strategies, and are willing to work hard.
Step 2: Figure out the role motor carriers and shippers play
The shipper is the party that has products to transport. As a freight broker, you will mainly deal with business companies.
A motor carrier is the party responsible for delivering the goods via truck to its destination. A freight broker negotiates a rate with a motor carrier.
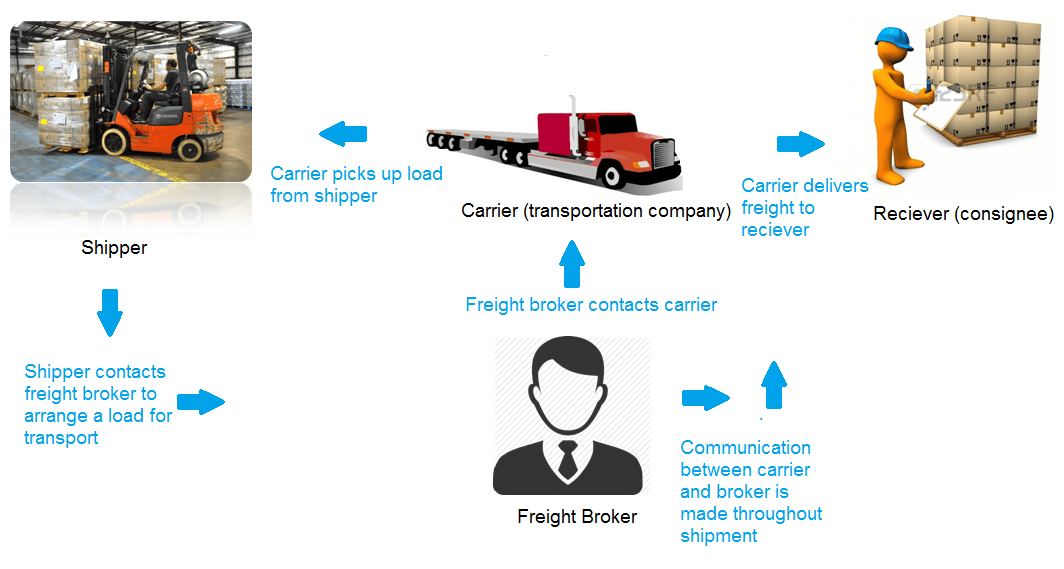
There are two types of carriers that you will need to know. Common carriers provide service to public under the responsibility of compulsory and liability for loss or damage to the load. A contract carrier moves cargo under a contract with shippers.
As a freight broker, you will need to establish good business relationships so that you don’t ever have a one-time customer.
Step 3: Know the types of trucks and trailers
The term “truck” is one that is applied to identify a variety of different trucks. In brief, they include flatbed, refrigerated (reefer), dry van (box truck), step deck, lowboy, double drop, and Conestoga. Read types of trucks and trailers to get more information.ste
Step 4: Decide on the type of freight you want to handle
Freight brokers have the option to choose what kind of cargo they want to control.
It is your choice if you wish to work with general loads or specialist loads.
Clients, who ship sensitive freight such as perishable goods or hazardous materials, have special hauling requirements.
Other requirements include verifying the hazmat description, labeling, marking, and certification.
Step 5: Create your business plan
How to create a business plan
While creating your business plan if you find that you don’t understand any key terms then refer to our glossary of transportation terms. Likewise, when writing your business plan avoid highly technical terms and diagrams.
1. Executive summary
The first step in creating a freight brokerage business plan is to write an executive summary. The executive summary serves as an introduction to your business.
2. Company Description
 The company description includes your mission statement, principal members, and legal structure.
The company description includes your mission statement, principal members, and legal structure.
Your mission statement is vital to your organization because it provides a clear understanding of the primary objective and keeps you and your team focused on the actual goals of the company.
For example, a good mission statement reads:
“ABC Freight Brokerage founded in 1999, is a strong regional brokerage based out of Seattle, Washington. As a leader in freight logistics, we are committed to high security, excellent customer service, and overall dependability. Let us integrate into your supply chain… as easy as ABC.”
3. Market research
The next step in developing your business plan is market research. Market research is integral to your business because it will identify your target market; find the geographical range you will be operating in, and develop a strategy to communicate with potential customers and investors.
Other information to take note of is your competitor’s price rates, the type of trucking technology they use, and the number of employees they have staffed.
4. Product/service outline
In this section, your business plan will discuss your service, pricing structure, and intellectual property rights.
Your freight brokerage business needs to have a clear and accurate outline of the service you provide. Write a brief paragraph detailing your service.
Next, you will need to determine a pricing structure for your freight brokerage.
Establishing a pricing structure is not an easy thing to do, but it is a crucial part of your business plan. Knowing what freight rates to charge your customers and pay your carriers will ultimately decide if your business can remain profitable.
As a freight broker, you will need to protect your intellectual property. For example, you may need to prevent a former employee from using your customer list.
Some companies who have not used any method to protect intellectual property see other competing businesses apply the same tactics.
5. Marketing and sales
The next step is to plan the marketing and sales portion of your business. Here, you will need to describe how your company will use marketing and sales strategies to acquire customers.
Outlining a growth strategy is more than just planning how you intend to grow your revenue numbers. In fact, potential investors and bankers will want to know how you plan on building your company after the initial launch.
Ways you can achieve growth in your company include opening multiple locations, introducing new clients’ bases, establishing freight contracts, hiring talented employees, or writing a value proposition.
Step 6: Form a Legal Structure
As mentioned earlier, forming a legal structure is important because it affects your financial liability, the amount of taxes you’ll pay, and how much control you have over your company. The legal structure details the ownership of a company. There are a number of options you have when forming the legal structure of your enterprise:
Sole proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest type of business to manage. To set up your business as a sole proprietorship you need to apply for the required licenses to do business in your local city and state. There is no need to apply for federal taxpayer identification (FTI) number. Instead, you can use your social security number to file your annual taxes. Simply report your company’s revenues and expenses on a Schedule C form and attach it to your tax return.
Step 7: Get insured
It is smart to sit down with your insurance provider each year to discuss the insurance needs of your business. Often, insurance companies will develop new packages that are beneficial to those who own a business in the transportation sector.
Conversely, a type of insurance policy that your freight brokerage is strictly advised to have is contingent cargo, vicarious liability, and general liability. You will need these three types of insurance policies because most shippers will request them and they will protect your business.
We recommends Reliance Partners or Truck Writers insurance firm for all your freight brokerage insurance needs.
Step 8: Learn to operate your business and manage necessary paperwork
Concept of Freight Brokering
The basic idea behind brokering freight is relatively straightforward. A shipper (also called the consignor) notifies your brokerage that they need a load moved. You complete your internal paperwork and check to see if any carriers in your network have an available truck.
If a carrier agrees to transport a load, their representative will sign and fax back the document. Once the carrier has dispatched the driver, get the driver to give you call notifying when the load is picked up and when it is delivered.
After the load is delivered, the carrier will fax (or email) you an invoice and the original bill of lading form. In turn, you will need to send an invoice to the shipper (customer). Next, you will need to pay the carrier.
Quoting and Negotiating rates
Quoting and negotiating rates is not an easy task. There are many different factors that go into developing a pricing structure.
However, the two primary factors that go into deciding freight charges are weight and distance. The type of trucking equipment needed is also a key factor. Moreover, the number of stops the driver will have to make to pickup or deliver the load also affects freight charges.
Startup Equipment Checklist
A major financial advantage freight brokers have is the low cost of starting up. There is little need to lease an elegant office. And there is also no need to buy expensive equipment such as a tractor-trailer. Ideally, all you need is a good home office setup.
The following highlights the right equipment and tools needed to get started as a freight broker:
- Computer and High-Speed Internet Access
This step is relatively straightforward and requires you to have a computer hooked up to high-speed internet. - Freight Broker Software
Utilizing freight broker software is optional but can save you tons of time when you’re filing paperwork. Our recommendation for the best freight broker software is Tailwind TMS - Phone line
Because you will need a method to cold call as well as talk to clients and contractors, you will need phone access. You may start off as using your home or cell phone as your primary phone line, then switch to a dedicated line after generating some revenue. - Metered mail machine
Avoid using postage stamps when sending mail because it does not portray a professional impression. Instead, opt for metered mail because it is the most appropriate for business applications. Metered mailing systems can be bought at Stamps.com. Postage meters are printed in a percentage of a cent which can equate to large savings if your business will be sending a lot of mail - Fax machine
A fax machine is a tool that will quickly pay for itself. Our recommendation is to purchase a multi-function printer that features a fax machine. - Paper shredder
Paper shredders will act as a security guard for all your paperwork. Shredders eliminate the risk that someone may find and use information on internal and confidential documents.
In conclusion, step 8 should give you enough information so you can start operating your brokerage. Continue reading further to find out about legal requirements.
Step 9: Obtain a USDOT number
If you are a freight broker that will be involved in interstate commerce, then you must apply for operating authority from the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). The FMCSA is a regulatory government agency that is a part of the U.S. Department of Transportation. It oversees interstate commerce and enforces safety rules.
However, upon completing the Unified Carrier Registration, you will need to pay an ongoing annual fee of $76/ per year. ste
To begin your application with the URS, click here.
Step 10: Get a Surety Bond or Trust Bond
Every freight broker is responsible for having a $75,000 surety bond or trust fund. If you are using a surety bond, fill form BMC-84. If you are using a trust fund, fill form BMC-85
Surety bonds are a three-party agreement between the principal (your freight brokerage) obligee (the FMSCA), and the surety (insurance company providing the bond). They are paid on an annual basis with a cost ranging from $500-$6000/ per year. Surety bonds need to be renewed every year.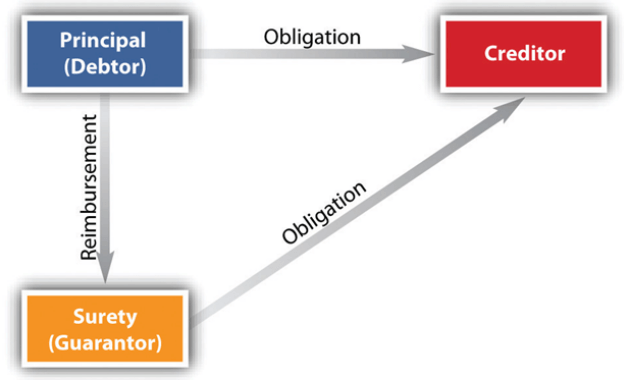
The purpose of a surety bond is to ensure that a freight brokerage follows all applicable laws and regulations and delivers on its promises. Essentially, it is an additional line of credit for your company.
Suppose if ever you are unable to pay a claim: in this case, the bonding company will pay the claim and require you to repay the bonding company within 90 days.
Premiums for surety bonds can range from 1.2% to 5%. The best way to reduce bond premiums is to have a good credit score.
Step 11: Designate a Process Agent
The next step in starting your freight brokerage is to appoint a process agent for your company.
A process agent is a person upon whom court papers may be issued to in the case a legal proceeding (lawsuit) is brought against the freight brokerage. Brokers must list process agents in every state they have an office location. They must also designate process agents in which states they write contracts.
Step 12: Build strong industry relationships and partnerships
Business is just as much about people as it is about profits.
Even though you may be the boss of your company, you are not expected to know everything, especially at the beginning. If are you are completing each step as directed, you have a high chance that you will succeed at freight brokering.
Other relationships you will need include carriers, shippers, bankers, insurance agents, attorneys, and accountants. fr
Step 13: Market your business and generate sales
Learning how to market your freight brokerage the right way is one of the main ways to convince carriers and shippers to do business with you.
Build a website
A solid looking website along with the right social media accounts should be a part of your marketing strategy. Through your site you can write articles that may convince your target customers to do business with you. Social media such as Facebook, LinkedIn, and forums are a great place to start promoting your brand.
Building a website for your freight brokerage will cost about one hundred and fifty dollars ($150). Here’s how to do it:
Simply go to the Hostgator website and follow the on-screen instructions. After you have signed up for Hostgator, refer to your email to retrieve your Cpanel login details. Enter your login details to the Cpanel link to access the backend. Next, click on QuickInstall and follow the on-screen instructions to install WordPress.
Once you have installed WordPress, you need to select a transportation theme. I prefer to use Themeforest where you can get a great looking theme for $30-$60. The theme I recommend is Logistic. You can also type in transportation into the ThemeForest search bar to view other themes. To upload the theme to your WordPress just click on Appearance> Themes > Add New. You can begin customizing and adding the required information to your new website!
Step 14: Manage finances
Although starting a freight brokerage does not require lots of cash to setup facilities and equipment, it does require enough cash flow so you can pay carriers on time. While most shippers will pay within a few days, certain shippers may take weeks to pay. In this scenario, you want to pay your bills on time. As a result, you will maintain a good business reputation in the market and this will entice new partners to work with you.
Establishing credit policies and procedures
Because you will be invoicing your customers (shippers) and/or consignee (receiver), you need to establish proper credit policies and procedures. When a freight broker agrees to move a load on behalf of the shipper before getting paid, he/she is extending credit to the shipper. You must have an assumption that the shipper intends and is capable of paying you.
Remember, trucking companies have to pay for fuel, insurance, drivers, and much more. Hence, cash flow is just as important for you as a broker as it is for the carrier.
Speak with your accountant to address your financial management needs.
Step 15: Grow your business
When you start your freight brokerage business you will learn valuable insights into how the transportation market operates. However, a time will come when your company will need to expand. Growing your business can mean hiring employees, moving into a commercial office, or increasing revenue and profit margins. A key point you want to take into consideration when expanding your business is to build a strong positive reputation. In the transportation industry, shippers, carriers, and other brokers will usually know each other. As a result, if your company’s performance is poor, don’t expect for word to not get around.
Step 16: Become a Certified Freight Broker
Much of what you have to know on how to become a freight broker or start a new brokerage business is covered in our freight brokering training guide. If you are following each step as described, I am confident you will succeed. You should ensure you get the right industry certifications to help you along your career. The Transportation Intermediaries Association (TIA) is a very well recognized organization that offers a novice freight broker course. It is at your discretion if you wish to enroll in this training.
Want a textbook manual on freight broker training? Use TruckFreighter.com’s exclusive guide available on Amazon to establish your brokerage.
Content constructed by: Mike Brar
Content marketed by: Julia P.




